We would like to bring to your attention a recent publication titled “Effects of sub-chronic donepezil on brain Abeta and cognition in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease”. This article in Psychopharmacology was authored by BMS in collaboration with reMYND:
Since its introduction 15 years ago, acetylcholinesterase inhibitors (AChEIs) are approved to treat the symptoms of Alzheimer’s disease by restoring acetylcholine levels at synapses. This assumption is challenged by more recent clinical studies suggesting the potential for disease-modifying effects of AChEIs. However, few preclinical studies have assessed whether the improvement of cognitive symptoms may be mediated by reductions in Abeta or Tau pathology.
The study in reMYND’s hAPP/PS1 mouse model showed a significant and dose-dependent improvement in reference memory along with similar reductions in brain amyloid-β (Aβ) following a short-duration treatment with donepezil starting at an age where amyloid pathology was fully developed, consistent with early stages of Alzheimer’s disease in humans.
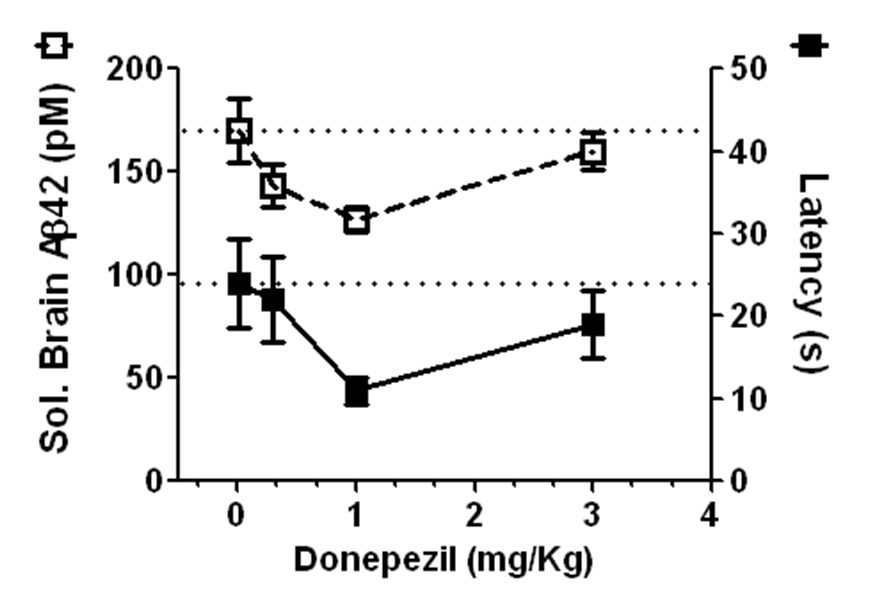
These results suggest that the observed cognitive improvement produced by donepezil in Alzheimer’s disease may be due, at least in part, to reduction of brain Aβ.
The full paper can be ordered here.
For more information on reMYND’s transgenic mouse models please visit our website or contact us at cro@remynd.com. You can also contact us at this email address to set-up a meeting the AAIC meeting in Boston from 13-18 July if you want to explore in-person how we could help you.
Kind regards,
The CRO team













