The interplay of Ab and Tau is still considered detrimental if not crucial for disease etiology and progression of Alzheimer’s Disease. You can now also assess the effects of your experimental Alzheimer’s Disease treatment on both amyloid- and tau pathology in the cross of our APP-london and Tau.P301S transgenic mouse models, in which APP-london aggravates the Tau-effect.
In the combined model expressing the human APP-london and human Tau.P301S heterozygous transgenes, progressive Tau pathology is observed in the hindbrain, midbrain, cortex and hippocampus (Figure 1, left). These animals exhibit a cognitive deficit at 6.5 months of age in the Morris water maze task (Figure 1, right) followed by a motor deficit at later age allowing for a longitudinal follow-up.
Compared to the single transgenic heterozygous Tau.P301S transgenic model, the double transgenic model shows an enhanced Tau pathology and cognitive deficit, suggesting that the expression of the APP-london mutant worsens Tau pathology.
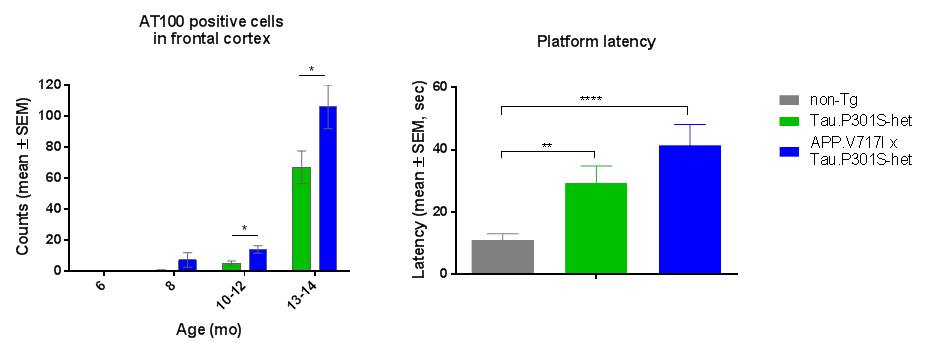
Figure 1: Comparison of Tau pathology (AT100 positive staining, left) and cognitive deficit (right) in the single transgenic Tau.P301S mouse model (green) and the double transgenic APP-london x TAU.P301S transgenic mouse model (in blue). Statistics: students T-test * p<0.05, ** p<0.01
For more information on reMYND’s transgenic mouse models or read-outs, please visit our website or contact Bart Roucourt, CRO Manager.
With kind regards,
The CRO team
[/html]













